Duma
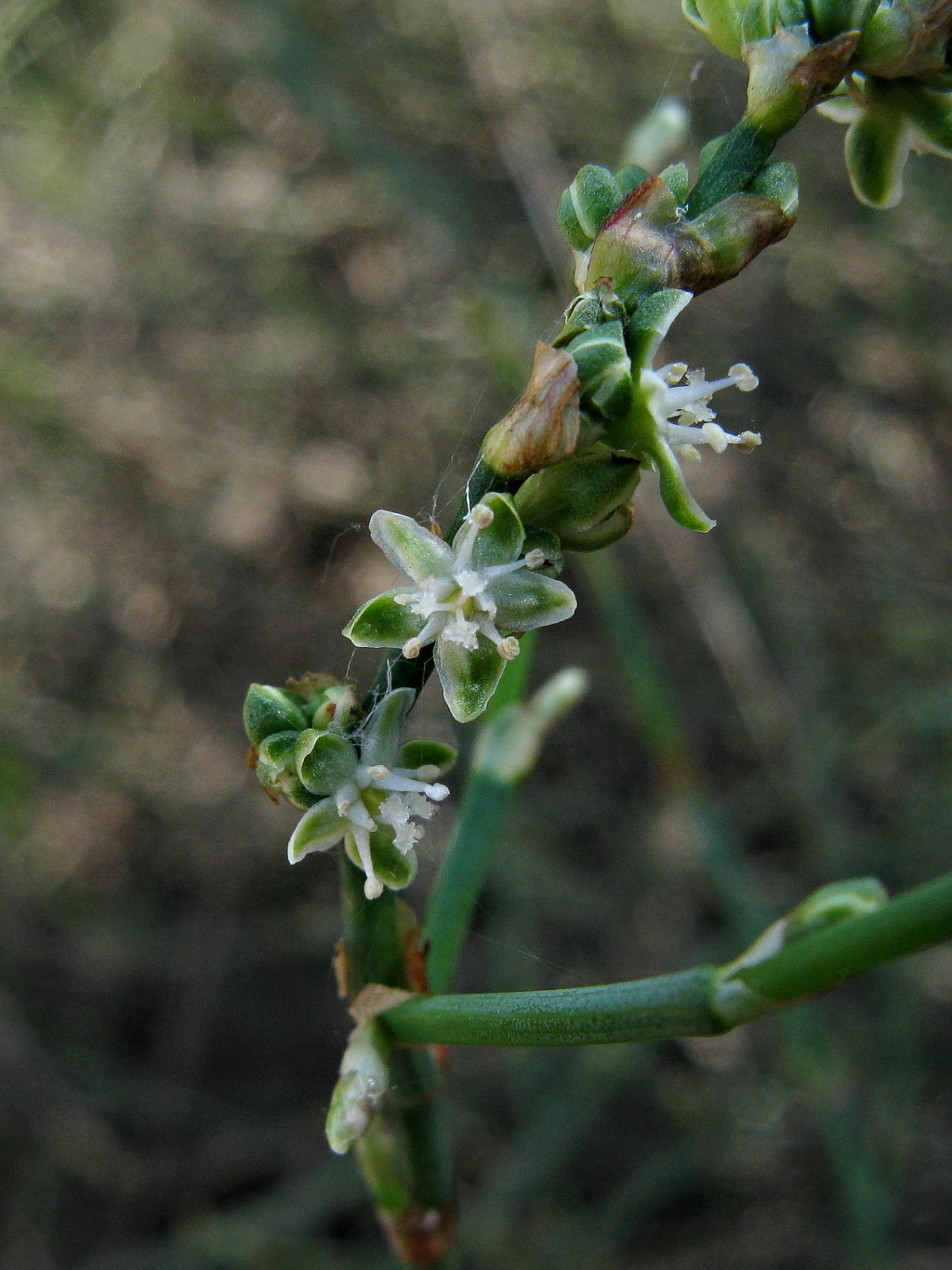
Much-branched, dioecious shrubs; branches terete, usually spine-tipped. Leaves deciduous, alternate, sessile or subsessile, articulate, linear or lanceolate; ochreas, short, tubular, brown, membranous, glabrous, soon disintegrating. Flowers unisexual, in spike-like inflorescences or in sessile clusters at nodes; perianth segments 5, sepaloid, green or creamy yellow, enlarged and fleshy in fruit; stamens 8 (staminodes present in female flowers); style 3-branched, stigmas flattened, peltately attached, fringed. Nut trigonous or ovoid, remaining at least partly enclosed within fruiting perianth.
3 species all endemic to Australia.
Members of this genus have recently been removed from Muehlenbeckia. Phylogenetic studies of selected members of the Polygonaceae family have shown taxa segregated into Duma are more closely related to Polygonum than to Muehlenbeckia (Schuster et al. 2011).
 Spinning
SpinningSchuster, T.M.; Wilson, K.W.; Kron, L.A. (2011). Phylogenetic relationships of Muehlenbeckia, Fallopia, and Reynoutria (Polygonaceae) investigated with chloroplast and nuclear sequence data. . International Journal of Plant Sciences 172(8): 1053–1066.