Geranium molle
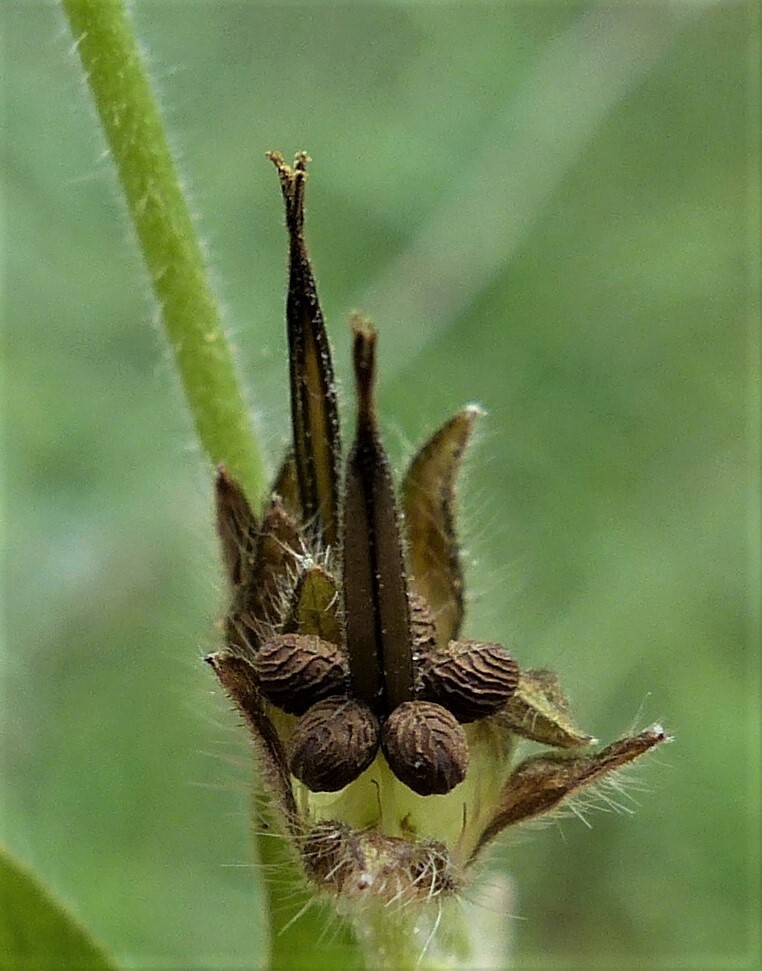
L.Prostrate to weakly ascending annual or short-lived perennial; stems to 50 cm long, subvelutinous, with short spreading glandular and eglandular hairs and longer spreading, shining eglandular hairs; taproot slender. Leaves often alternate, orbicular to reniform, 0.5–3 cm long, palmatifid with 5–9, broad, trifid (or weakly further divided) lobes; ultimate lobes truncate to obtuse; upper surface pilose; petioles to 8(–20) cm long; stipules narrow-ovate to oblong, lacerate to laciniate. Flowers paired; peduncle 1–4 cm long; pedicels to 2.4 cm long; sepals ovate to elliptic, 4–5 mm long, villous with short glandular and longer eglandular hairs, mucro absent or to 0.5 mm long; petals strongly emarginate, equal to or slightly longer than sepals, pink-magenta; anthers mauve. Fruit 8–11 mm long, rostrum with very short glandular and longer eglandular hairs; mericarps transversely wrinkled, mostly glabrous, sparsely ciliate at base; seed virtually smooth. Flowers Sep.–Jan.
GleP, Brid, VVP, VRiv, MuF, GipP, OtP, WaP, Gold, CVU, GGr, DunT, NIS, EGL, EGU, WPro, HSF, HNF, OtR, Strz, VAlp. Also naturalised in WA, SA, Qld, A.C.T., NSW, Tas. Widespread on disturbed or cultivated land (gardens, lawns, crops etc.), or in waste places, particularly common on sandy soils. Native to Europe, northern Africa and western Asia.
Possibly imported into Australia in stock feeds. Geranium aequale (Babington) Aedo is found in New South Wales, Tasmania and New Zealand, and could be expected to appear in Victoria. This species differs from Geranium molle in having smooth mericarps.
 Spinning
Spinning