Dawsonia
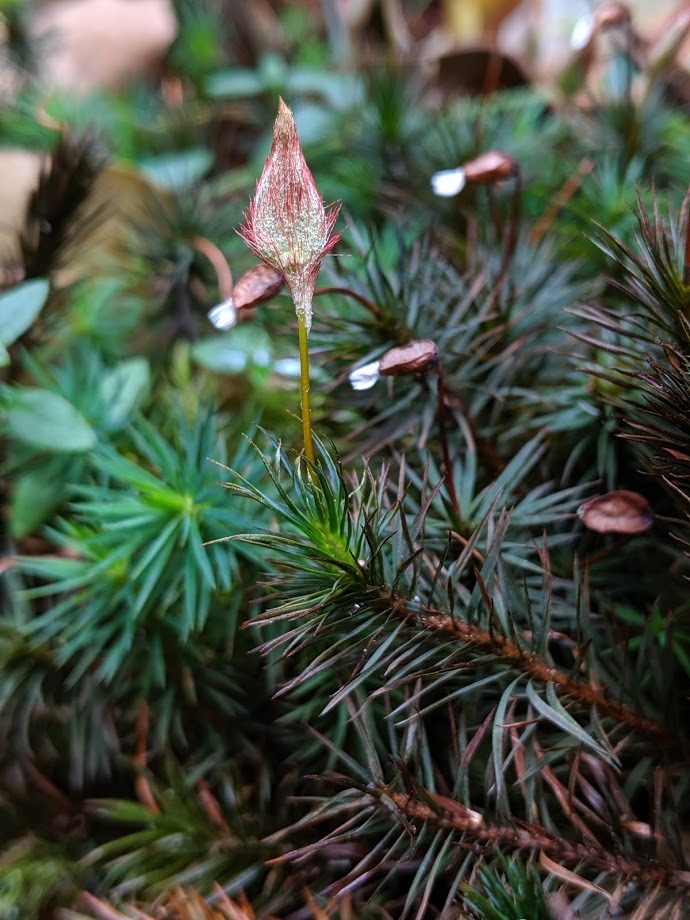
Dioicous. Aerial stems simple, forked or rarely fastigiately branched, to 65 cm tall, with dense whitish rhizoids at base; central strand with hydroids only or of both hydroids and sclerenchyma. Leaves scale-like at base, larger toward apex, lingulate or linear from a clearly sheathing base, caniculate, plane or spirally twisted, erect-spreading to wide-spreading when moist, appressed when dry, with most of adaxial surface covered with lamellae, except for up to 5 rows of cells along margins; lamellae 2–10 cells tall; apex acute; costa ill-defined, broad; margin serrate, plane or involute; laminal cells rectangular, rectangular or linear in sheath, striate-papillose or smooth. Capsule erect becoming inclined or horizontal when mature, ovoid, 2-angled, flattened or concave dorsally, convex ventrally, with stomata at base. Calyptra cucullate, with a dense mat of entwining branched serrate hairs, initially enveloping entire capsule and sometimes upper seta. Operculum conic. Peristome of numerous long filiform teeth, forming a white or dirty white brush-like tuft, not attached to an epiphragm.
Nine species shared between Malesia from Mindanao and Borneo east to the Solomon Islands and eastern Australia and New Zealand, but most diverse in New Guinea where seven species have been recorded (van Zanten 1973); three species in Victoria.
 Spinning
SpinningZanten, B.O. van (1973). A taxonomic revision of the genus Dawsonia R.Brown. *Lindbergia * 2: 1–48.