Molluginaceae
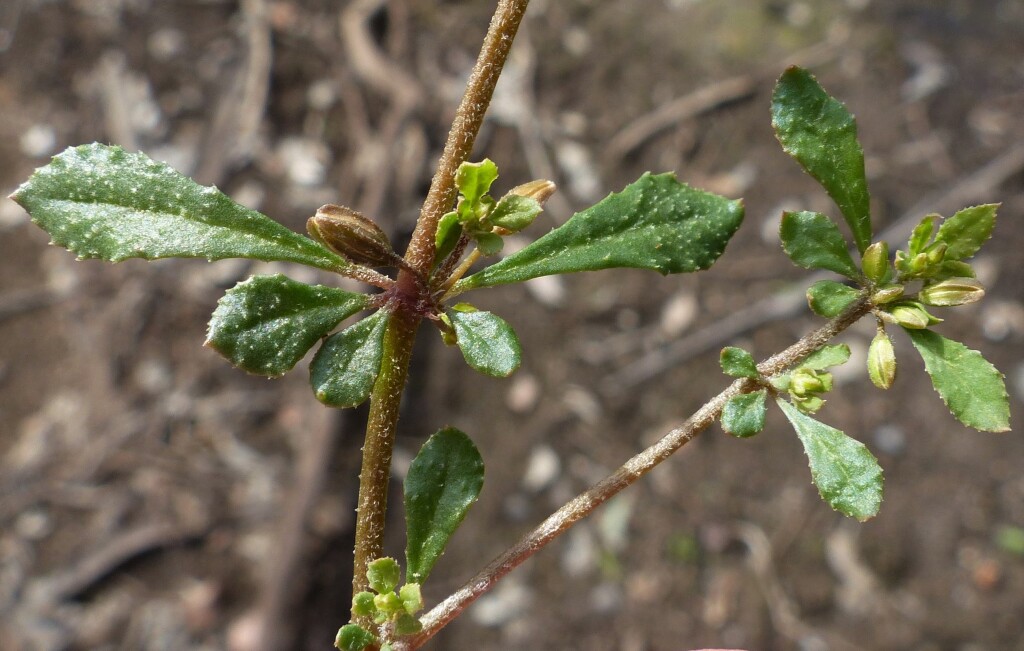
Annual or perennial herbs, rarely subshrubs. Leaves opposite, alternate or whorled, simple and entire; stipules usually absent or small and deciduous, rarely large and incised. Flowers usually small and inconspicuous, in cymes, or solitary in axils, bisexual, or rarely unisexual, regular; perianth of a single whorl of (4–)5, free segments (rarely the segments united into a tube below); stamens 2–20 (but usually equal to or twice as many as perianth segments); anthers opening via longitudinal slits; ovary superior, 2–5-locular; styles usually as many as locules; ovules 1–several per locule. Fruit a dry capsule opening by longitudinal or transverse slits.
About 13 genera and 100 species mainly in tropical and subtropical regions, chiefly Africa; about 12 species, mostly native, in 3 genera in Australia.
The Molluginaceae is sometimes treated as a subfamily (Molluginoideae) within a broader concept of the Aizoaceae than that adopted here.
Walsh, N.G. (1996). Molluginaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 3, Dicotyledons Winteraceae to Myrtaceae, pp. 225–228. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning