Mesembryanthemum cordifolium
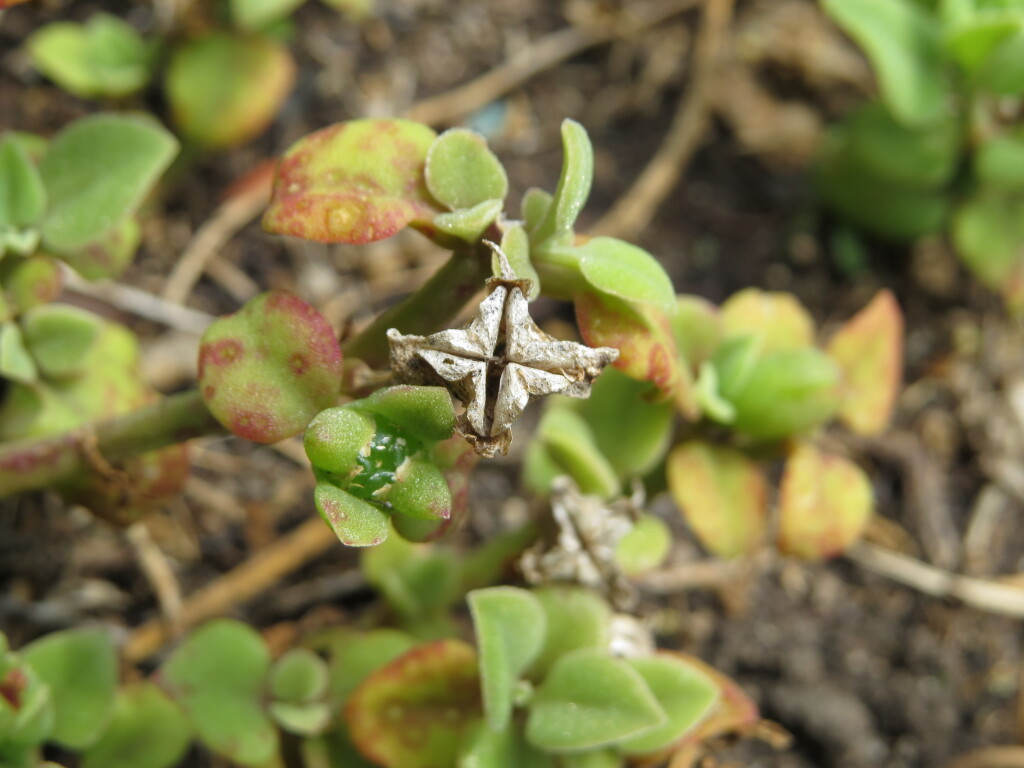
L.f. Heart-leaf Ice-plantSucculent perennial herb with scrambling or prostrate stems to 1.2 m long, minutely papillose, somewhat brittle. Branches angular (4-angled). Leaf lamina (10–)15–26(–35) mm long, 10–20(–25) mm wide, usually cordate or broad ovate with somewhat truncate or obtuse base, some younger leaves can be ovate in plants with otherwise mostly cordate adult leaves, margin entire, apex acute (to obtuse), lamina mid green, often glossy, minutely papillate; petiole to 5–12 mm long. Pedicels 5–10 mm long, elongating in fruit; larger sepals ovate at anthesis, 9–11 mm long, 5–6 mm wide; smaller sepals linear or narrowly triangular, to 5–7 mm long, 3 mm wide; sepals enlarging in fruit. Flowers (8–)12–15 mm across. Staminodes deep pink or magenta. Stamens with filaments white, anthers pale yellow. Stigmas 1.5–1.7 mm long. Capsule shorter than calyx, obconic, 9–12 mm long, 4–9 mm wide, glossy green, later dry and brown. Seeds many, very hard, ± circular, with a flattened dorsal ridge, prominently tuberculate, 1–1.5 mm diam., brown. Flowers sporadically throughout the year, with a peak in mid to late summer and into autumn.
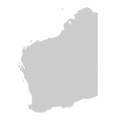
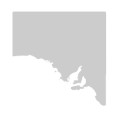
MuM, VVP, VRiv, GipP, OtP, CVU, EGL, HSF. MuM, VVP, VRiv, GipP, OtP, CVU, EGL, HSF. Also SA, NSW, Tas. Occurs in coastal sites (Melbourne area, Lakes Entrance, Marlo) and drier areas inland where saline or rocky (e.g. far northwest, Craigieburn, Keilor, Heyfield).
The widely cultivated Mesembryanthemum × vascosilvae (Gideon F.Sm., E.Laguna, Verloove & P.P.Ferrer) L.Sáez & Aymerich ‘Red Apple’ which is an artificial hybrid of garden origin, obtained from a crossing of Mesembryanthemum cordifolium and Mesembryanthemum haeckelianum A.Berger (Smith et al 2019a; Smith et al. 2020) is often confused with Mesembryanthemum cordifolium. Several cultivars of Mesembryanthemum × vascosilvae are available, ‘Red Apple’ being the most common cultivar that is seen in cultivation (including in Australia). Mesembryanthemum × vascosilvae ‘Red Apple’ is much more widely cultivated than its parent species, and it has largely replaced M. cordifolium in domestic and amenity gardening (Smith et al. 2019a). The author (V. Stajsic) has not observed either of the parent species in cultivation in Victoria. Mesembryanthemum cordifolium is distinguished from M. × vascosilvae ‘Red Apple’ by its usually cordate or broad ovate leaves with somewhat truncate or obtuse bases, and the papillae on the leaves are more conspicuous. The leaves in M. × vascosilvae ‘Red Apple’ are usually ovate with obtuse bases, and the papillae are less conspicuous. Based on the Victorian observations of naturalised plants of M. cordifolium and the cultivated plants of M. × vascosilvae ‘Red Apple’, the leaves in M. cordifolium tend to be smaller (10–)15–26(–35) mm long and 10–20(–25) mm wide, whereas the leaves in M. × vascosilvae ‘Red Apple’ are usually 35–45 (–60) mm long and 20–33 mm wide. The staminodes in M. cordifolium are usually magenta, whereas the staminodes in M. × vascosilvae ‘Red Apple’ are usually strawberry red, but the intensity of the flower colour in M. × vascosilvae ‘Red Apple’ can vary slightly (Smith et al. 2019a). There also appears to be a slight difference in the size of the flowers, (8–)12–15 mm across in M. cordifolium and 15–20 mm across in M. × vascosilvae ‘Red Apple’. Mesembryanthemum × vascosilvae ‘Red Apple’ is not known to be naturalised in Victoria, but it is adventive in South Australia. Overseas, M. × vascosilvae ‘Red Apple’ is naturalised in Italy (Di Gristina et al. 2021), Portugal (Smith et al. 2019b), Spain (Serapio et al. 2023), and USA (California, Oregon) (Vivrette 2003).
Di Gristina, E., Domina, G. & Barone, G. (2021). The alien vascular flora of Stromboli and Vulcano (Aeolian Islands, Italy). Italian Botanist 12: 63–75. https://italianbotanist.pensoft.net/article/74033/ [Date Accessed: 05 August 2024]
Sáez, L. & Aymerich, P. (2020). A new nomenclatural combination in Mesembryanthemum L. (Mesembryanthemoideae, Aizoaceae). Butlletí de la Institució Catalana d’Història Natural, 84: 71.
Serapio, J., Laguna, E., Gómez-Bellver, C., Domínguez, L.A., Verloove, F. & Sáez, L. (2023). Contribution to the alien flora of the Balearic Islands. Butlletí de la Institució Catalana d’Història Natural 87(1): 11–28.
Smith, G.F., Silva, V. & Figueiredo, E. (2019a). Aptenia ‘Red Apple’ (Aizoaceae / Mesembryanthemaceae), a common cultivar derived from a hybrid between two Aptenia species endemic to southern Africa. Bradleya 37: 179–183.
Smith, G.F., Silva, V. & Figueiredo, E. (2019b). Representatives of Aptenia N.E.Br. (Aizoaceae / Mesembryanthemaceae), an endemic southern African genus, naturalised in Portugal. Bradleya 37: 184–190.
Smith, G.F., Laguna, M., Verloove, F. & Ferrer-Gallego, F. (2020). Aptenia × vascosilvae (A. cordifolia × A. haeckeliana) (Aizoaceae), the new nothospecies from which the horticulturally popular cultivar Aptenia ‘Red Apple’ was derived. Phytotaxa 441(2): 221-224.
Venning, J. & Kodela, P.G. Mesembryanthemum cordifolium, in P.G. Kodela (ed.), Flora of Australia. Australian Biological Resources Study, Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water: Canberra. https://profiles.ala.org.au/opus/foa/profile/Mesembryanthemum%20cordifolium [Date Accessed: 05 August 2024]
Vivrette, N.J. (2003) Aptenia, in Flora of North America Editorial Committee, Flora of North America 4: Magnoliophyta: Caryophyllidae, part 1, pp. 83–84. (New York Oxford. Oxford University Press).
 Spinning
Spinning