Cunoniaceae
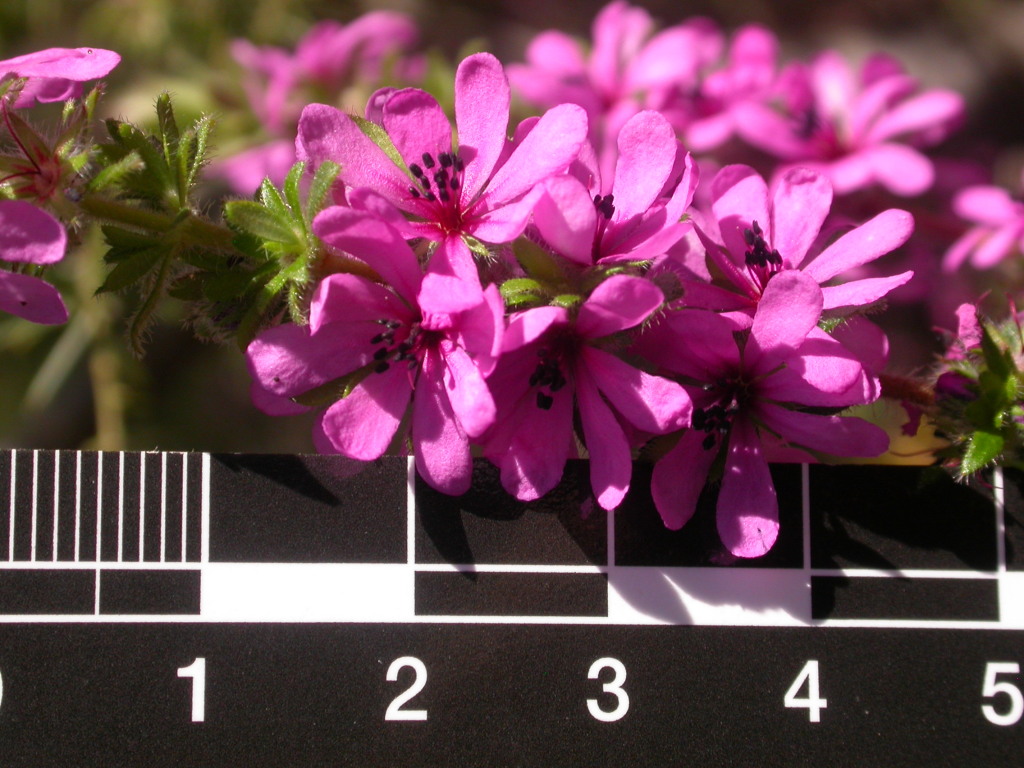
Shrubs, trees or woody climbers. Leaves opposite, whorled or alternate, simple, pinnate, trifoliolate or palmate, margins often with gland-tipped teeth; interpetiolar stipules sometimes present, caducous. Inflorescence a panicle, raceme or head, rarely flowers solitary in axils; flowers bisexual (rarely unisexual), actinomorphic; sepals (3–)4–5(–10), free or variously fused; petals more than or equal in number to and usually smaller than sepals, sometimes absent; stamens mostly twice as many as sepals, with filaments longer than petals (when present), anthers opening via vertical slits; ovary superior or semi-inferior, mostly 2–5-locular; ovules 2–many per locule. Fruit usually a capsule, rarely nut-like or a drupe or follicle; seeds small, commonly winged or hairy.
29 genera and c. 280 species, mainly Southern Hemisphere; 15 genera with 38 species in Australia.
Now includes Eucryphiaceae.
Walsh, N.G. (1996). Cunoniaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 3, Dicotyledons Winteraceae to Myrtaceae, pp. 524–526. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning