Banksia marginata
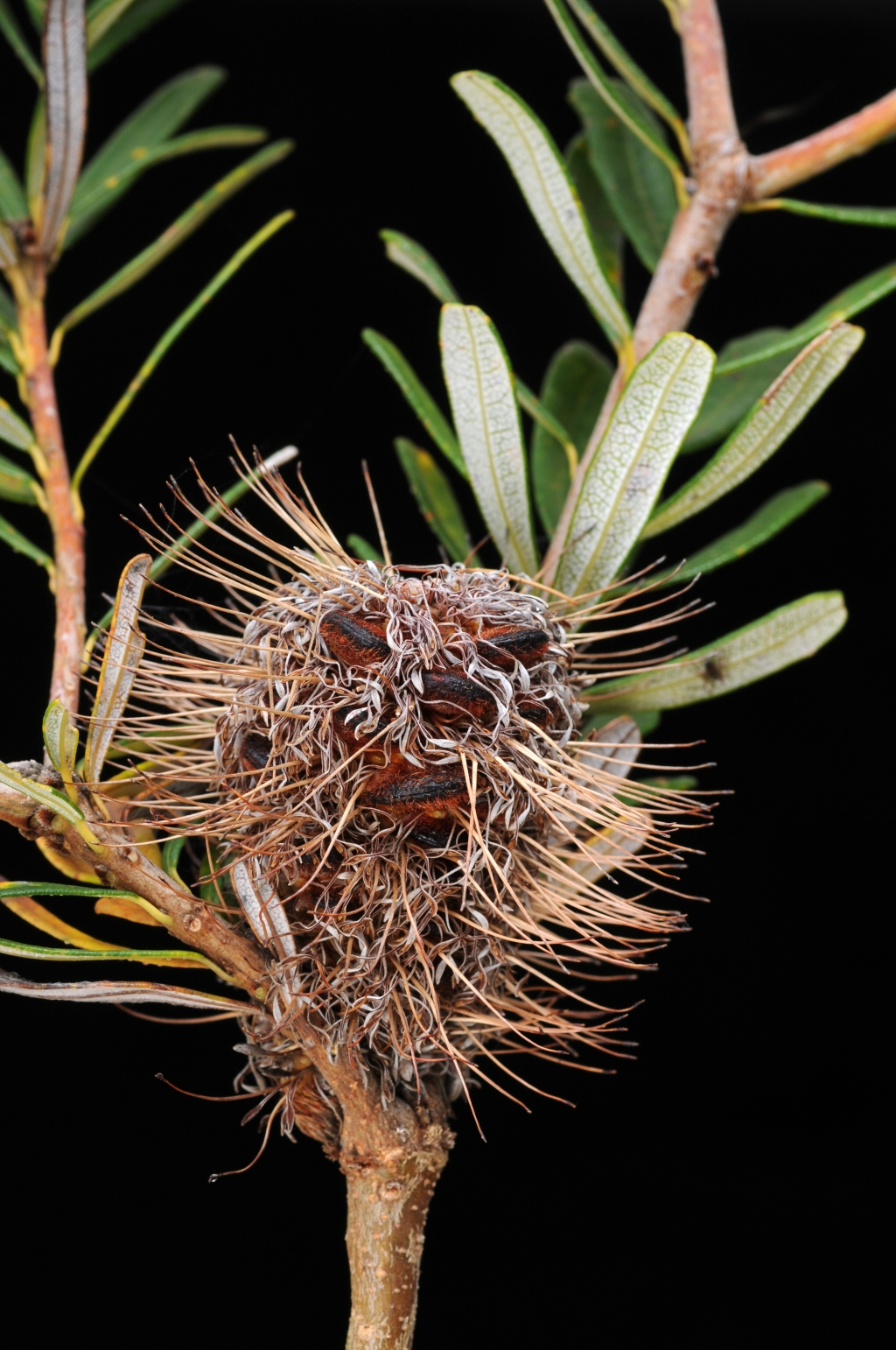
Cav. Silver BanksiaShrub or tree to c. 12 m high; lignotuber present or absent; bark thin, brown, sometimes thick and tesselated on taller trees; branchlets hirsute with spreading and/or short curled hairs. Leaves alternate, scattered, linear, oblong, narrowly cuneate or lanceolate, 1–8 cm long, 3–15 mm wide, discolorous, upper surface dark green, lower surface white-tomentose; margins entire or sometimes with a few serrate leaves persisting, more or less flat, recurved or revolute; apex obtuse, truncate or emarginate, mucronate; petiole 2–5 mm long. Inflorescence 3–13 cm long, 4–6 cm wide at anthesis. Tepals 16–24 mm long, pale yellow, hairy, persistent; style straight or gently curved, persistent. Follicles to c. 150, 7–17 mm long, hirsute, becoming glabrous, usually opening when mature. Body of seed more or less cuneate, 5–8 mm long, wing to c. 15 mm long. Flowers mainly Feb.–Jul.
LoM, MuM, Wim, GleP, Brid, VVP, VRiv, GipP, OtP, WaP, Gold, CVU, GGr, DunT, NIS, EGL, EGU, WPro, HSF, HNF, OtR, Strz, MonT, HFE, VAlp. Also SA, NSW, ACT, Tas. Except for the far north-west, widespread and often locally common throughout Victoria in a wide range of habitats.
A very variable species in terms of habitat, habit, leaf shape and indumentum. Possible hybrids with Banksia saxicola have been observed in the Grampians.
Jeanes, J.A. (1996). Proteaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 3, Dicotyledons Winteraceae to Myrtaceae, pp. 830–887. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning