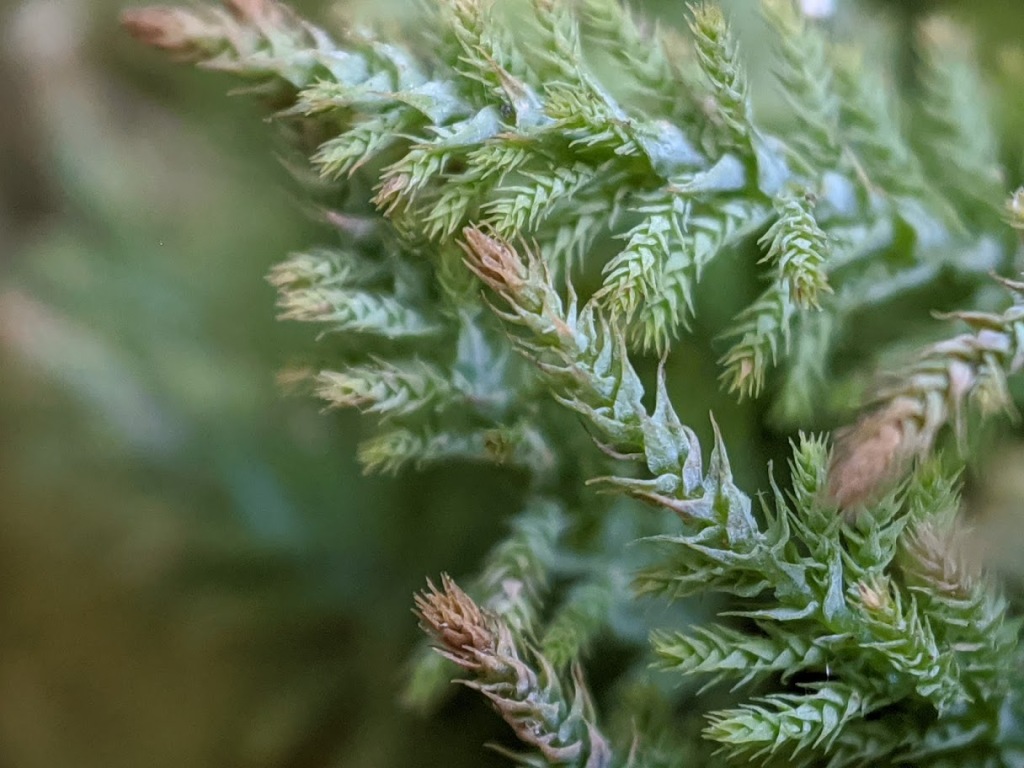
Philonotis scabrifolia
(Hook.f. & Wilson) Braithw.Loose or dense tufts on soil or occasionally rock. Stems 10–30 mm long, pinnately or irregularly branched, often with an unbranched lower part, covered with brown rhizoids at base. Leaves erecto-patent to wide-spreading when moist, appressed when dry, lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate; stem leaves 0.7–1.3 mm long, 0.36–0.97 mm wide; branch leaves smaller, 0.36–0.75 mm long, 0.15–0.36 mm wide; apices acuminate, commonly incurled; costae excurrent; margins serrulate to denticulate, plane or slightly recurved, without a border; laminal cells short-rectangular to subquadrate, 10–26 μm long, 8–10 μm wide, papillose. Setae 15–20 mm long, orange-brown. Capsules usually horizontal, ovoid, curved, 2–2.5 mm long. Opercula conic, umbonate. Peristome double.
MuM, Wim, VVP, VRiv, GipP, Gold, CVU, GGr, NIS, EGL, EGU, HSF, HNF, Strz, VAlp. Also WA, SA, NSW, ACT and Tas. New Guinea, New Zealand, Lesotho, South Africa, Central and South America, and Auckland, Crozet, Falkland, Kerguélen, Marion, South Georgia and Tristan da Cunha Islands. Widespread along and south of the Great Dividing Range usually close to streams, but also in moist sites among rocky areas and roadsides.
 Spinning
SpinningGilmore, S.R. (2006). Philonotis. Flora of Australia 51: 265–270.