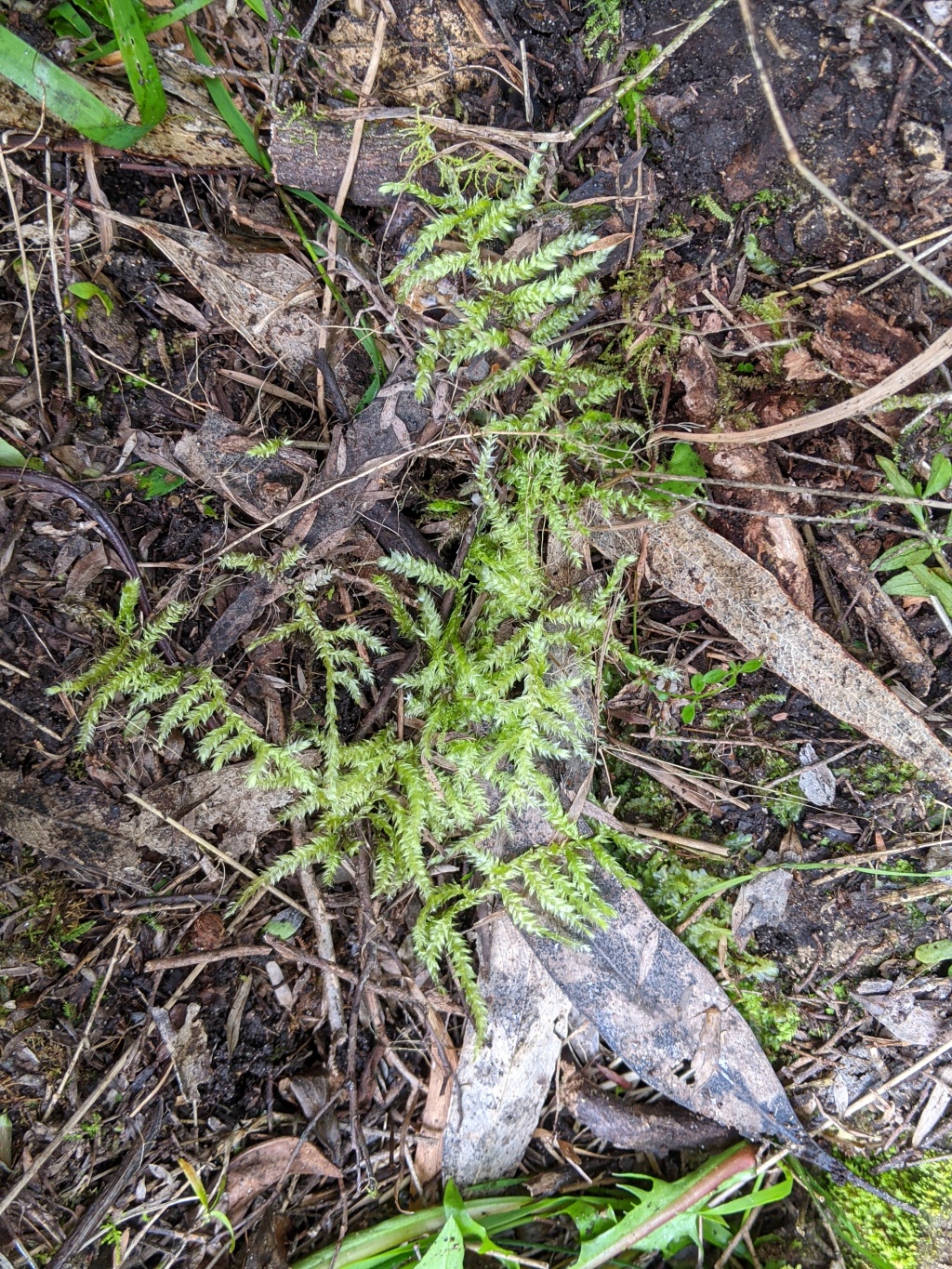
Rhynchostegium tenuifolium
(Hedw.) ReichardtInterwoven mats on soil, logs, tree bases and rarely rocks, green or yellow green. Stems usually c. 40–100 mm long, creeping, prostrate, irregularly or subpinnately branched, with ascending branches, yellow, with fascicles of brown rhizoids on ventral surface, central strand present. Stem and branch leaves differing by size, wide-spreading, broadly ovate, plane; costae extending 35–75% of leaf length, long costae occasionally ending in abaxial spine; apices acuminate; margins denticulate near base or apex, plane; cells linear, mostly (44–) 52.5–136.5 (–147) μm long, 5–8.5 (–9.5) μm wide, smooth; alar cells not differentiated; stem leaves mostly (1.6–) 1.8–2 mm long, c. 1 mm wide, not complanate; branch leaves mostly 1.5–1.6 (–1.8) mm long, 0.65–0.8 mm wide, more complanate than stem leaves. Setae (10–) 18–42 mm long, red-brown, smooth. Capsules horizontal, short-cylindric, curved, 1.6–2 mm long. Operculum long-rostrate from conic base, 1.6–2 mm long.
GleP, Brid, VVP, VRiv, GipP, OtP, WaP, Gold, CVU, GGr, DunT, NIS, EGL, EGU, WPro, HSF, HNF, OtR, Strz, MonT, HFE, VAlp. Widespread from the inland slopes of the Great Dividing Range south, most commonly beside creeks or rivers but also in a wide range of other habitats such as rainforest, wet-sclerophyll forest, open forest and moist sites among coastal vegetation. Also WA, SA, Qld, NSW, ACT and Tas. New Zealand and South America.
 Spinning
Spinning