Pluchea
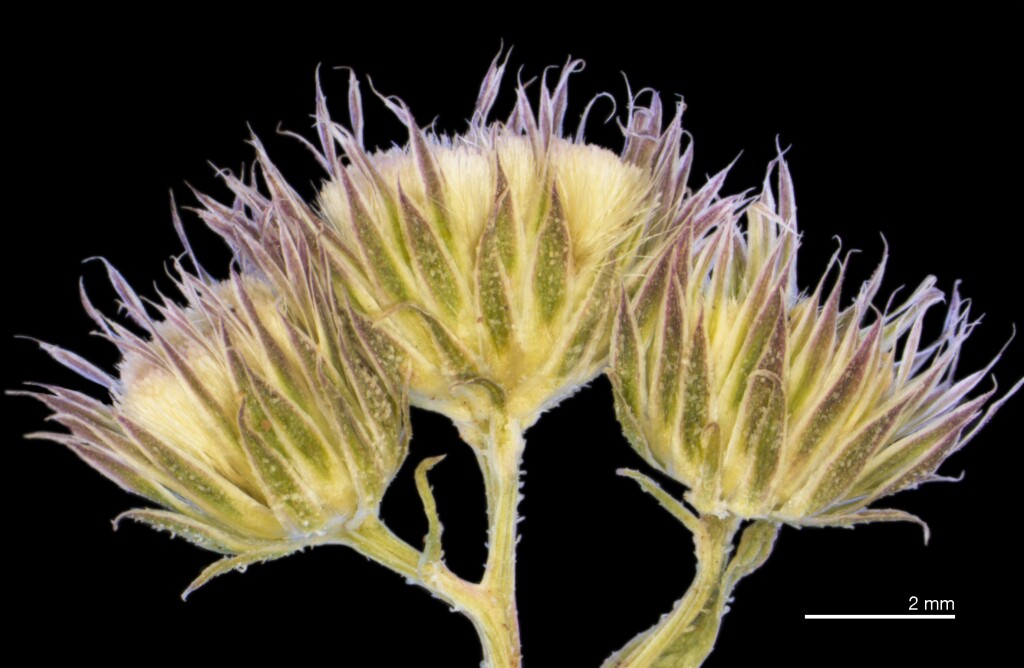
Annual or perennial herbs or shrubs, usually aromatic. Stems terete, or winged from decurrent leaf bases. Leaves simple, alternate, sessile or petiolate; margins entire, toothed or lobed; glabrous or glandular-pubescent, lower leaf surface often with yellow sessile glandular hairs. Capitula simple, solitary on terminal peduncles or in terminal panicles, shortly pedunculate, disciform, homogamous or heterogamous; involucral bracts unequally 3–4-seriate, the inner bracts longer than outer bracts; receptacle flat to slightly convex, naked. Florets all tubular. Outer (i.e. marginal) florets female, filiform, numerous, corolla 2- or 3-toothed, white to pink; style branches filiform, glabrous; achenes subterete and often slightly compressed, smooth, not beaked; pappus of free uniseriate capillary bristles. Disc florets fewer, bisexual or functionally male, tubular, 4- or 5-merous, corolla tube white to pink; anthers tailed at the base; style entire or 2-lobed at the apex, papillose; achenes usually abortive, or fertile in some species, glabrous or with scattered appressed twin hairs; pappus of free capillary bristles all of similar length, persistent or caducous.
A genus of about 50 species, found mainly in tropical and subtropical parts of the world; 13 species occuring in Australia, 12 endemic.
 Spinning
SpinningBean, A.R. (2015). Pluchea. In: Wilson, A., Flora of Australia Volume 37, Asteraceae 1, pp. 408–417. ABRS/CSIRO Publishing, Canberra/Melbourne.