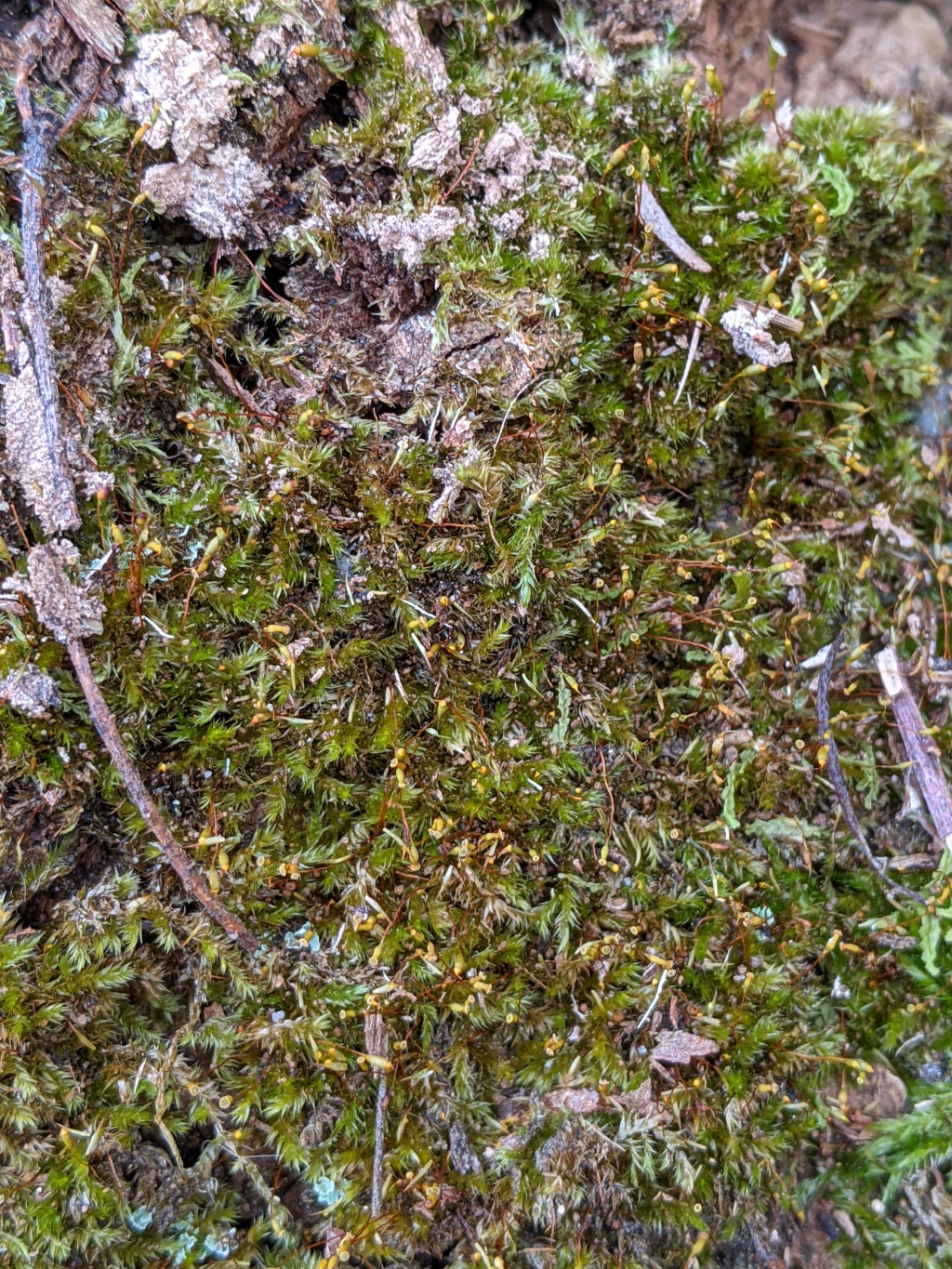
Sematophyllum homomallum
(Hampe) Broth.Dioicous. Asexual propagules absent. Dense, glossy mats on rocks or tree trunks or branches. Stems to 3 cm long, creeping, irregularly pinnate with somewhat cuspidate branches, with numerous fascicles of rhizoids on ventral surface. Leaves strongly homomallous, oblong or broadly ovate-lanceolate, 1.25–2 mm long, 0.4–0.65 mm wide, concave, erect spreading when moist, similar when dry; costa absent; apex acute, often weakly reflexed; margins entire, slightly recurved; cells linear-rhombic, 40–95 μm long, 4–7 μm wide; alar cells in 3 or 4 rows in alar angles, enlarged, irregularly quadrate, 22–65 μm long, 12–33 μm wide, orange or yellow, extending up margin 6–8 (–10) cells. Seta 5–8 mm long, yellowish orange, smooth. Capsule cylindric, ovoid or oblong, erect, straight, 1.2–1.75 mm long. Operculum finely rostrate from conic base, c. 1 mm long.
LoM, MuM, Wim, GleP, VVP, RobP, MuF, GipP, OtP, WaP, Gold, CVU, GGr, DunT, EGL, WPro, HSF, HNF, OtR, HFE. Particularly common in coastal and near-coastal areas throughout Victoria, usually in Leptospermum or Banksia woodland, but also among sclerophyll forest and woodland in some inland areas (e.g. the Grampians, Mt Arapiles, Murray River). Also WA, SA, QLD, NSW and Tas. New Zealand, Sri Lanka, Malesia and New Caledonia.
 Spinning
Spinning