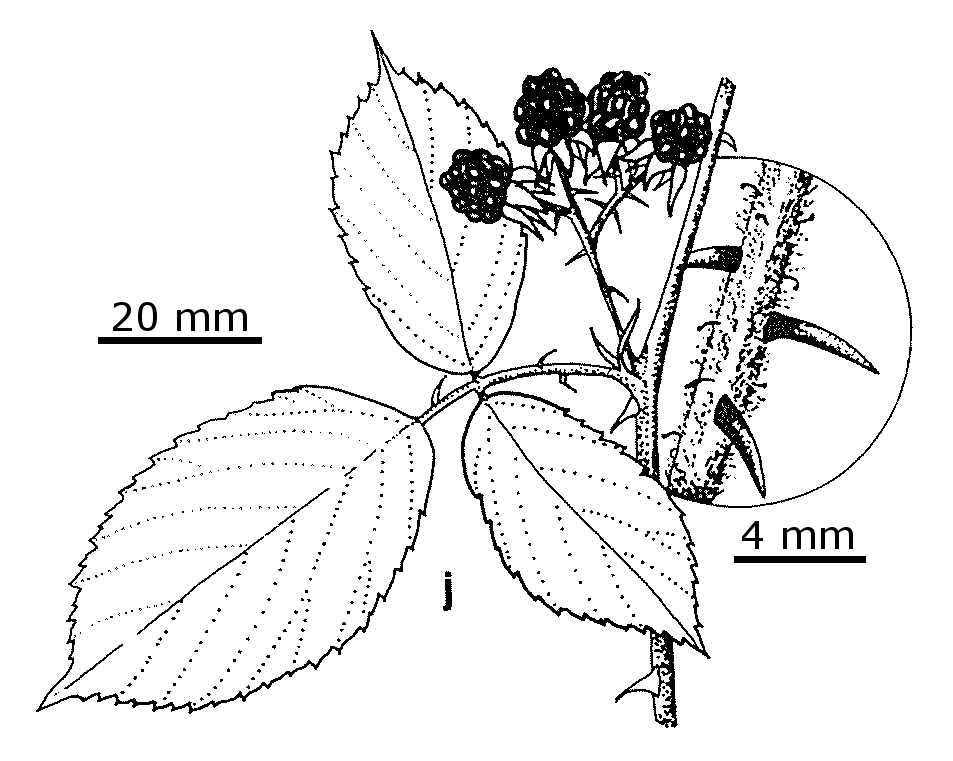
Rubus polyanthemus
Lindeb. BlackberrySemi-erect mound-forming shrub; stems arching, 1–2 m long, angular, glabrescent to moderately pubescent; prickles more or less equal, straight to falcate, subulate, to c. 6 mm long. Leaves (1–)3–6(–7)-foliolate; leaflets obovate to suborbicular, mostly 3–8 cm long, 2–6 cm wide, cuspidate, base cuneate, margins sharply and shallowly toothed, upper surface green, glabrescent, lower surface grey-tomentose or pubescent, at least some lower leaves with leaflets green and glabrescent below; stipules linear, pilose. Flowers in long, terminal racemes; axis and peduncles tomentose or pubescent, with stalked glands less than 0.5 mm long. Sepals grey-tomentose and pubescent, appendiculate, reflexed in fruit; petals suborbicular, white or pink; stamens much exceeding styles. Fruiting head more or less globose, c. 10 mm diam.; fruit glabrescent, black, not falling from receptacle when ripe. Flowers summer.
GleP, VVP, GipP, OtP, WaP, Gold, CVU, GGr, DunT, NIS, EGL, EGU, HSF, HNF, OtR, Strz, MonT, HFE, VAlp. Also naturalised NSW. Native of north-west Europe. In Victoria, known from widely scattered locations where usually found in cool, moist riparian habitats.
Jeanes, J.A.; Jobson, P.C. (1996). Rosaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 3, Dicotyledons Winteraceae to Myrtaceae, pp. 556–585. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
SpinningEvans, J.K.; Symon, D.E.; Whalen, M.A.; Hosking, J.R.; Barker, R.M.; Oliver, J.A. (2007). Systematics of the Rubus fruticosus aggregate (Rosaceae) and oher exotic Rubus taxa in Australia. Australian Systematic Botany 20: 187–251.