Bignoniaceae
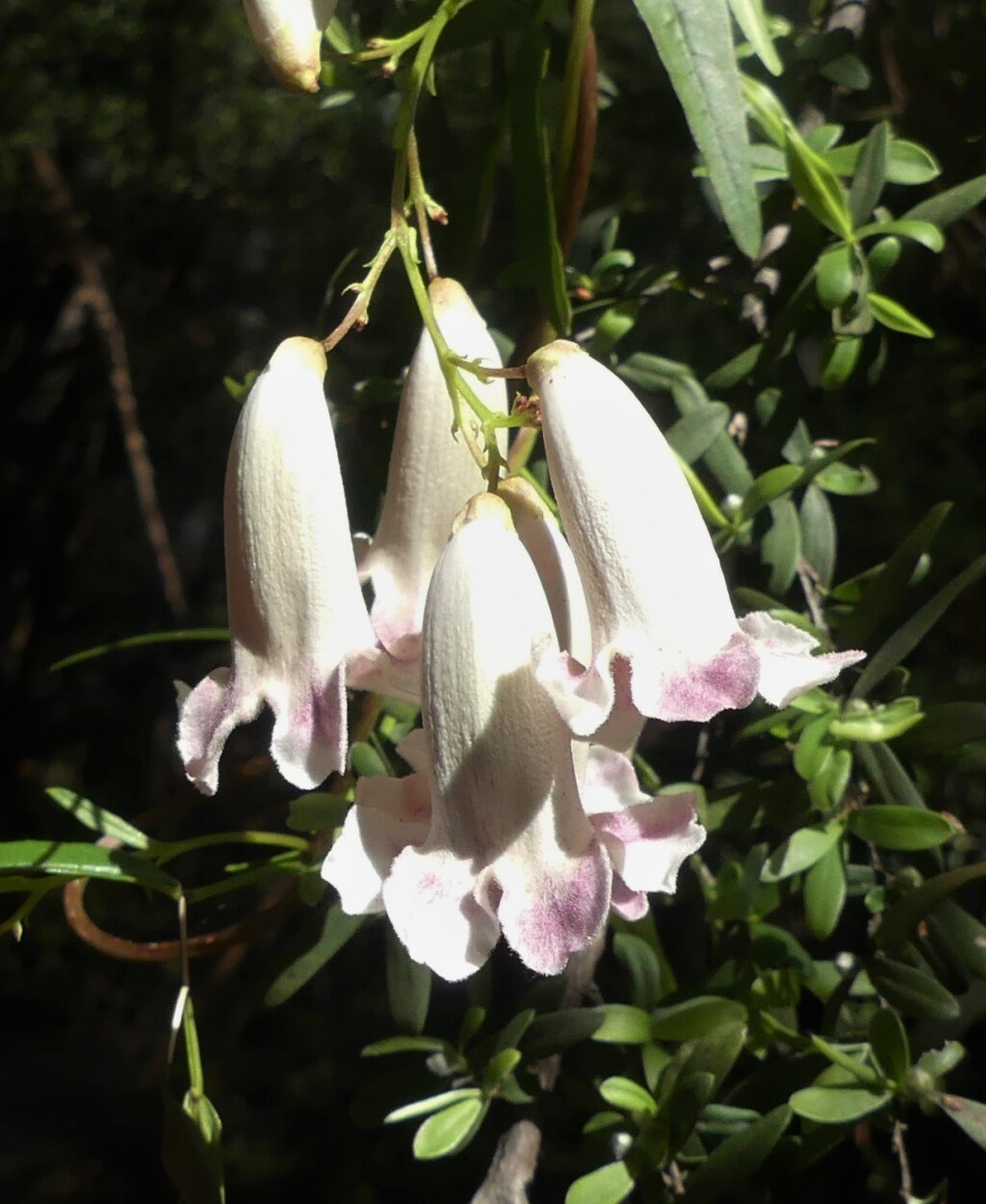
Trees, shrubs or woody climbers, rarely herbs. Leaves opposite or rarely whorled, simple or pinnately compound, sometimes with tendrils, usually glandular below; stipules absent. Inflorescence upper-axillary or terminal, cymes or racemes, or flowers solitary. Flowers more or less zygomorphic, bisexual, usually showy, often subtended by a bract and 1 or 2 bracteoles; calyx tubular, 5-lobed or truncate; corolla tubular, 5-lobed, often 2-lipped; stamens attached to base of corolla-tube, usually in 2 pairs of unequal length, or 2 stamens only (1 or 3 staminodes often present), anthers basifixed, 2-celled, opening by longitudinal slits; disc usually present, annular; ovary superior, elongate, usually 2-celled, ovules many per cell, style simple, stigma 2-lobed. Fruit a loculicidal or septicidal 2-valved capsule, rarely fleshy and indehiscent; seeds many, usually flat with a hyaline wing.
About 120 genera with c. 800 species, chiefly in tropical and subtropical regions, rarely extending to temperate regions; 10 genera in Australia.
Jeanes, J.A. (1999). Bignoniaceae. In: Walsh, N.G.; Entwisle, T.J., Flora of Victoria Vol. 4, Cornaceae to Asteraceae, pp. 546–547. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
 Spinning
Spinning