Syzygium
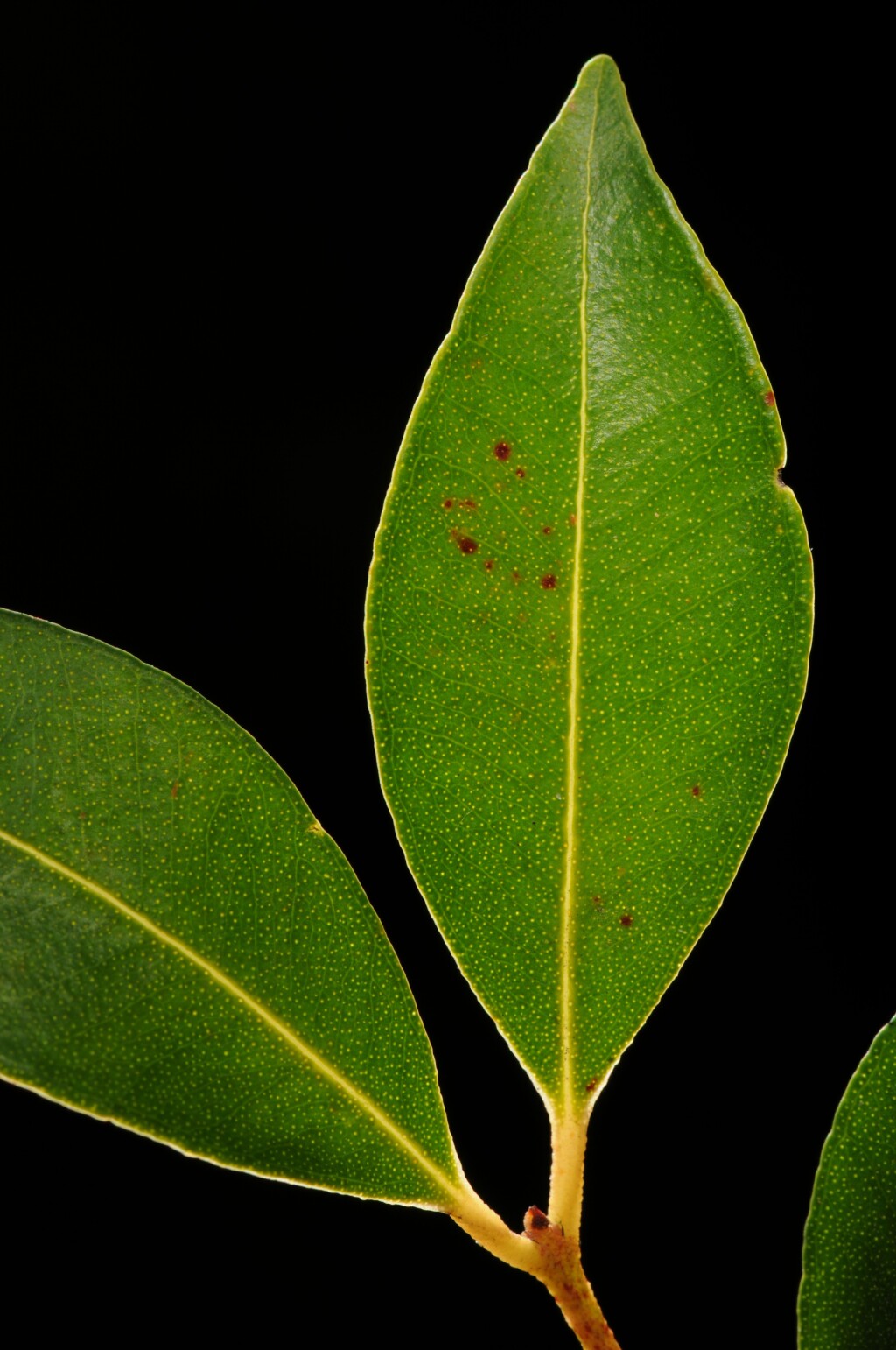
Trees or shrubs. Leaves opposite (juveniles and subadults sometimes slightly offset), petiolate, prominently veined. Inflorescence a terminal panicle. Calyx-lobes 4 or 5, smaller than petals; petals 4 or 5, more or less orbicular, sometimes irregular, sepals and petals sometimes united into calyptra (not in Victoria); stamens numerous, anthers reniform with divergent lobes (in Victoria) or anthers linear with parallel lobes; style usually shorter than stamens, stigma small; ovary almost inferior, usually 2–celled. Fruit a firm, usually spherical berry crowned by remains of floral tube; seed usually solitary, testa absent (in Victoria) or soft, leathery or papery, cotyledons fused (in Victoria) or distinct.
About 540 species from the tropics and subtropics, 76 species in Australia (2 naturalised).
Acmena DC. is generally now included in Syzygium (Craven et al. 2006). However, Acmena is still treated as a distinct genus in New South Wales and Queensland.
 Spinning
SpinningSynonyms
Craven, L.A.; Biffin, E.; Ashton, P.S. (2006). Acmena, Acmenosperma, Cleistocalyx, Piliocalyx and Waterhousea formally transferred to Syzygium (Myrtaceae). . Blumea 51: 131–142.