Grimmiaceae
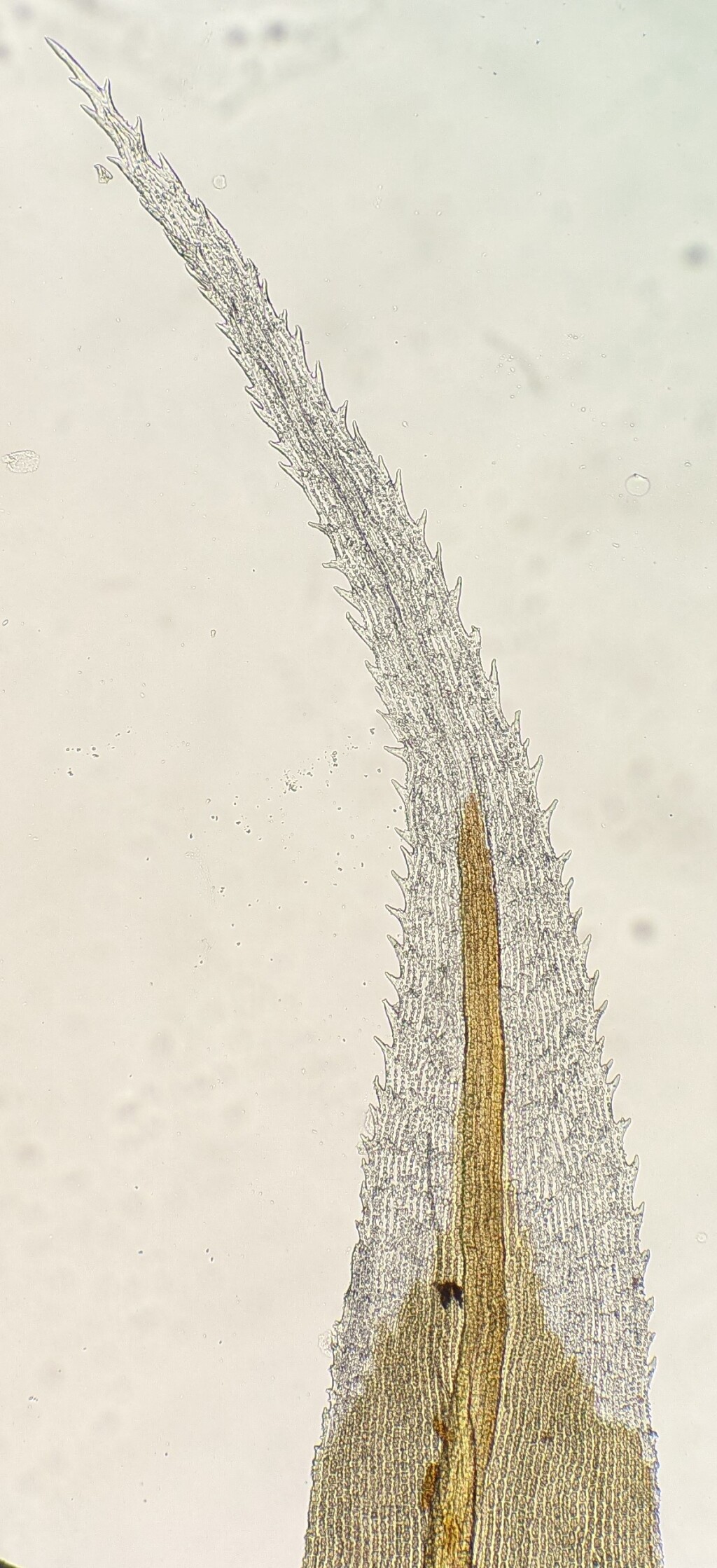
Autoicous or dioicous. Asexual reproduction occasionally by gemmae on leaves. Dense cushions, turves or mats on rock, rarely on soil or trees. Stem creeping, ascending or erect, dichotomously, irregularly or pinnately branched, rarely simple; central strand present or absent. Leaves arranged around stem and facing all directions, monomorphic, erect to squarrose when moist, appressed, falcate-secund, sometimes twisted, or rarely crisped (not in Victoria) when dry; apex rounded, acute or acuminate, hyaline or concolorous, hyaline tip sometimes decurrent down margins, often with a hairpoint; costa ending in mid-leaf (not in Victoria) or subpercurrent to excurrent; margins entire or denticulate or serrate near apex, plane, incurved or recurved, without a border or rarely with a border of pellucid cells near base (not in Victoria); laminal cells unistratose or multistratose toward apex, oblate to elongate, with straight or sinuose walls, smooth or papillose; alar cells undifferentiated or enlarged (not in Victoria). Acrocarpous or cladocarpous. Capsule erect to pendent, immersed to exserted, symmetric or slightly asymmetric, operculate; calyptra mitrate or cucullate, glabrous; operculum conic or rostrate. Peristome a single series of 16 teeth, sometimes also with a preperistome, or rarely absent (not in Victoria), with or without a basal membrane; teeth entire or divided into two or three segments in apical third to almost to base.
Cosmopolitan, with four genera and around 320 species, but most diverse in temperate regions; four genera and 15 species in Victoria.
 Spinning
Spinning